Ampere S Law In Integral Form
Ampere S Law In Integral Form - Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b → around a closed path in vacuum is equal to μ 0 times the total. Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: Establish ampere' law in integral form. Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. The law in integral form. Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the.
The law in integral form. Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b → around a closed path in vacuum is equal to μ 0 times the total. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: Establish ampere' law in integral form.
R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. Establish ampere' law in integral form. Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: The law in integral form. Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b → around a closed path in vacuum is equal to μ 0 times the total. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law.
Electrodynamics L7 Ampere law, integral and differential form YouTube
R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. The law in integral form. Establish ampere' law in integral form. Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current.
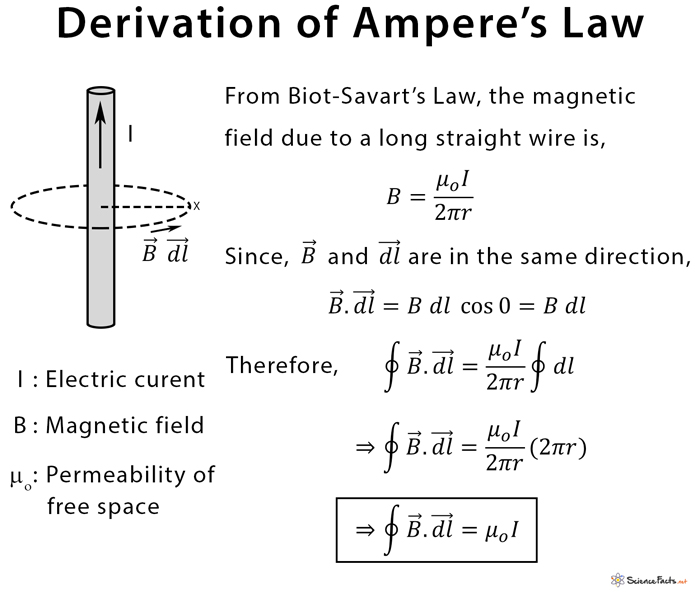
Ampere’s Law Differential form of ampere’s law Integral form of
Establish ampere' law in integral form. Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. The.
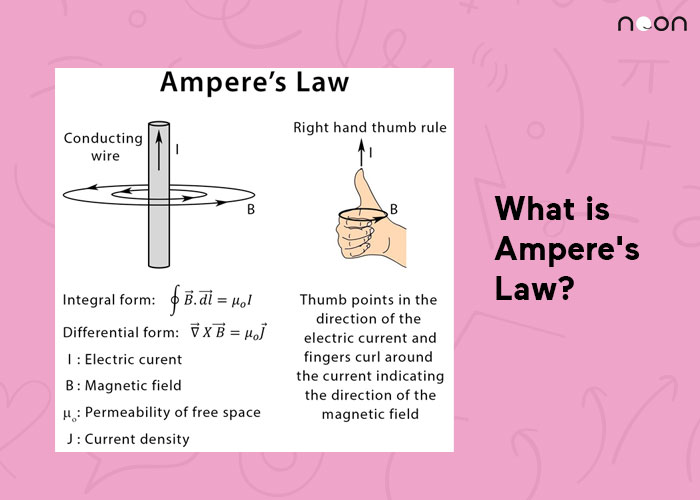
What is Ampere's Law? Noon Academy
Establish ampere' law in integral form. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: The law in integral form. R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the.
Ampere's Law Definition, Equation, and Application
Establish ampere' law in integral form. Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b → around a closed path in vacuum is equal to μ 0 times the total. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. The law in integral form.
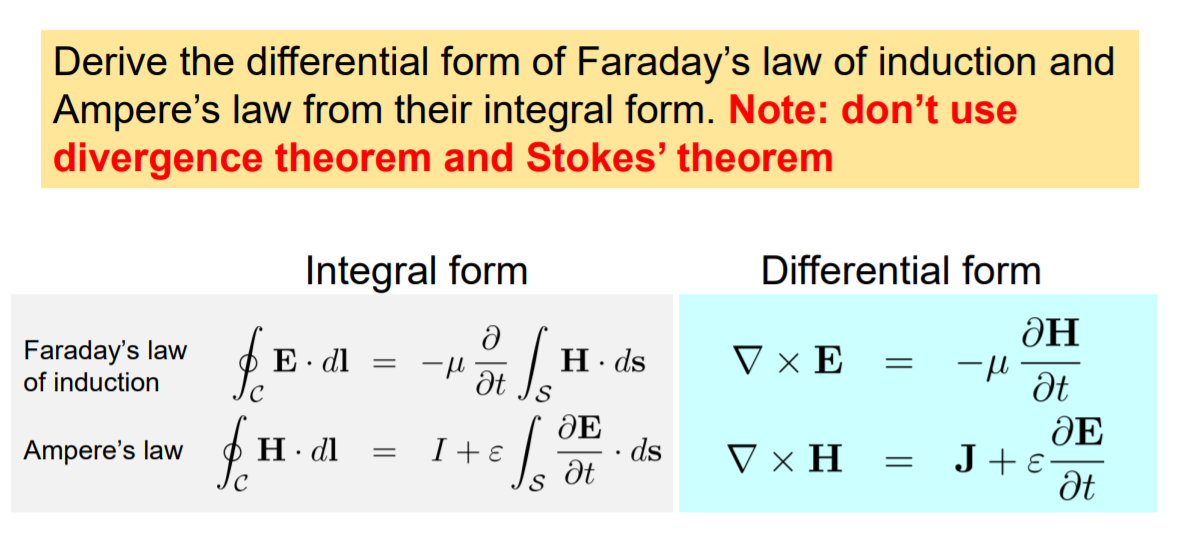
Solved Derive the differential form of Faraday's law of
Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. The law in integral form. Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b → around a closed path in.
Ampere's law (integral form) YouTube
Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b → around a closed path in vacuum is equal to μ 0 times the total. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration.
Ampere's Law (Integral Form) YouTube
Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b → around a closed path in vacuum is equal to μ 0 times the total. Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. Use the.
Solved How do you mathematically derive this
Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. The law in integral form. Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field induction b →.
PPT BiotSavart Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4065417
Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b.
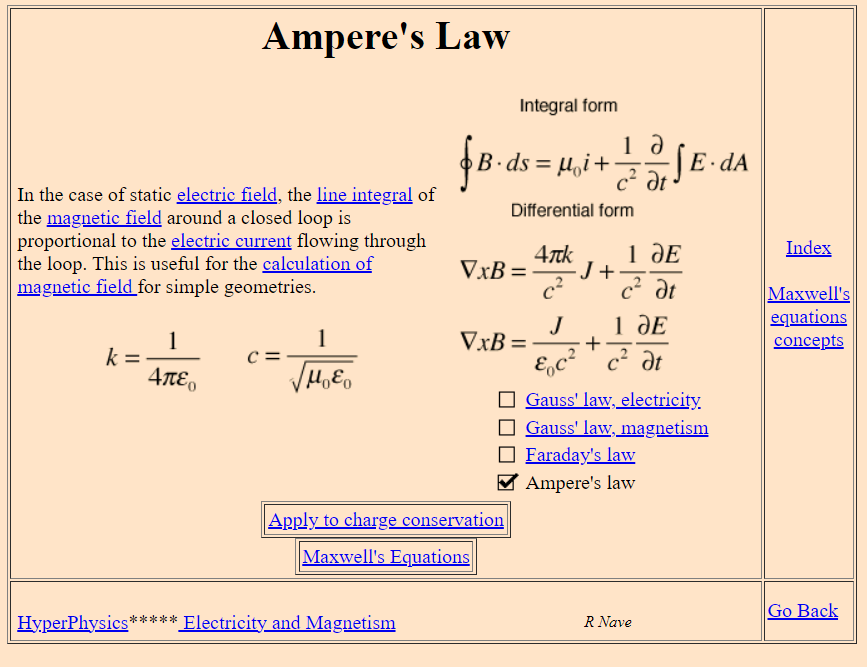
Ampere's Law Maxwell Equation Max Parr
Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. Establish ampere' law in integral form. R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. Everything's better with ampère's law (almost everything). Now, lets apply these results.
Ampere’s Circuital Law States That The Line Integral Of Magnetic Field Induction B → Around A Closed Path In Vacuum Is Equal To Μ 0 Times The Total.
Calculate the magnetic field for certain current configuration using ampere's law. R() ()ˆ 0 enc cc vv∫∫b ⋅= ⋅=dbad iaaφφρµ where you will recall that i enc is the. Use the integral form of ampere’s law, take an “amperian” loop contour c, enclosing the filamentary line current i as shown in the figure. Establish ampere' law in integral form.
Everything's Better With Ampère's Law (Almost Everything).
The law in integral form. Now, lets apply these results to the integral form of ampere’s law: