Cognitive Subtraction
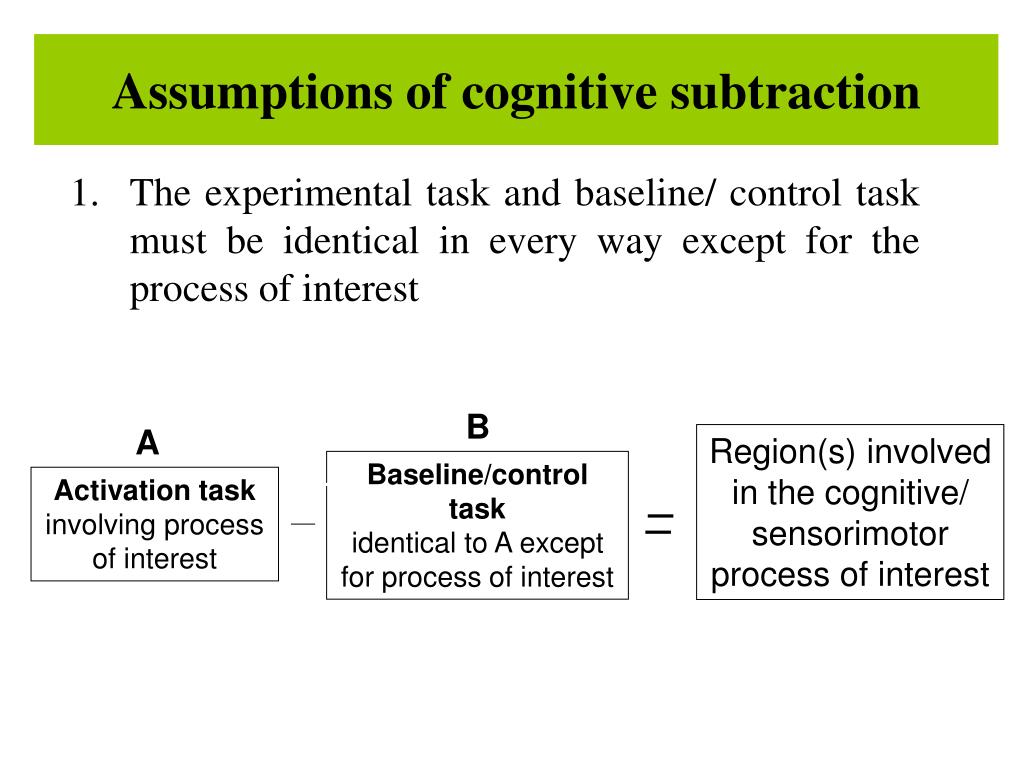
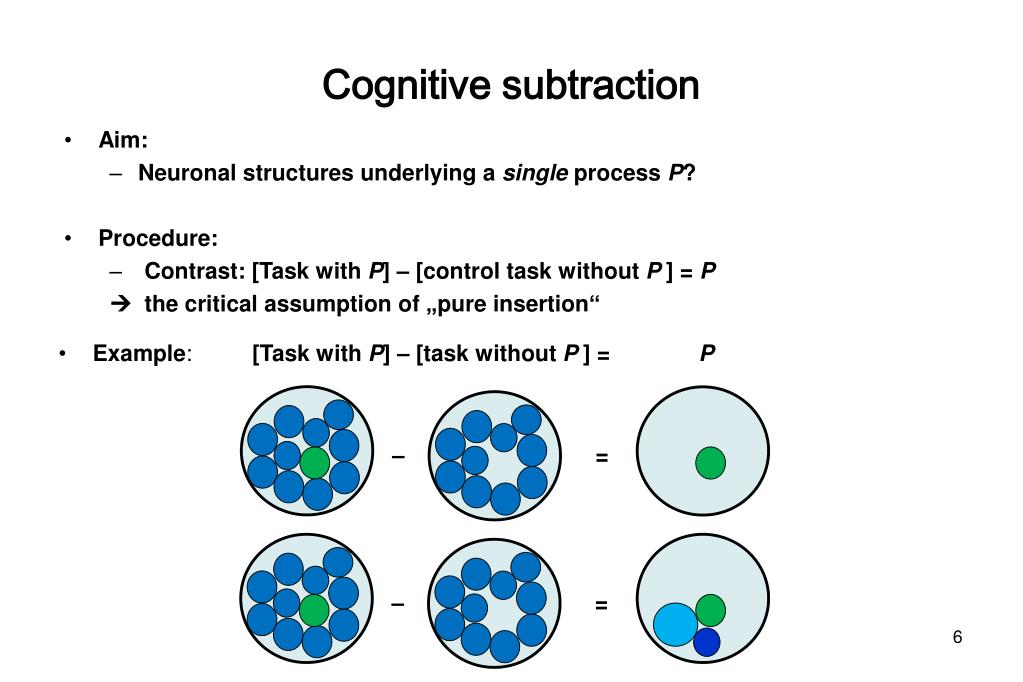
Cognitive Subtraction - In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task.
Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion.
Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion.
Cognitive Development Subtraction YouTube
In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction.
5 Cognitive Subtraction example 4 On the other hand, when the initial
In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a.
Cognitive subtraction YouTube
In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. In this paper we.
4 Cognitive Subtraction example 3 the annealed particle filter used
In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a.
3 Cognitive Subtraction example 2 when the robot has only modeled a
In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a.
PPT Contrast and Inferences PowerPoint Presentation, free download
In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction.
Cognitive subtraction ''foreign language (a) minus native language
Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas.
PPT Experimental design of fMRI studies PowerPoint Presentation, free
Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a.
2 Cognitive Subtraction example 1 in the presence of considerable
Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. In this paper we.
7/10/2014 Yingying. MRI studies brain anatomy. Functional MRI (fMRI
In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an experimental task. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction.
Functional Neuroanatomy Of Cognitive Processes Is Generally Derived By Subtraction Of A Control Task From An Experimental Task.
In cognitive subtraction, the area of activation is identified by subtracting one task from another, whereas in cognitive conjunction an area of. Functional neuroanatomy of cognitive processes is generally derived by subtraction of a control task from an. In this paper we present a critique of pure insertion.