Cognitive Theory Of Learning Definition
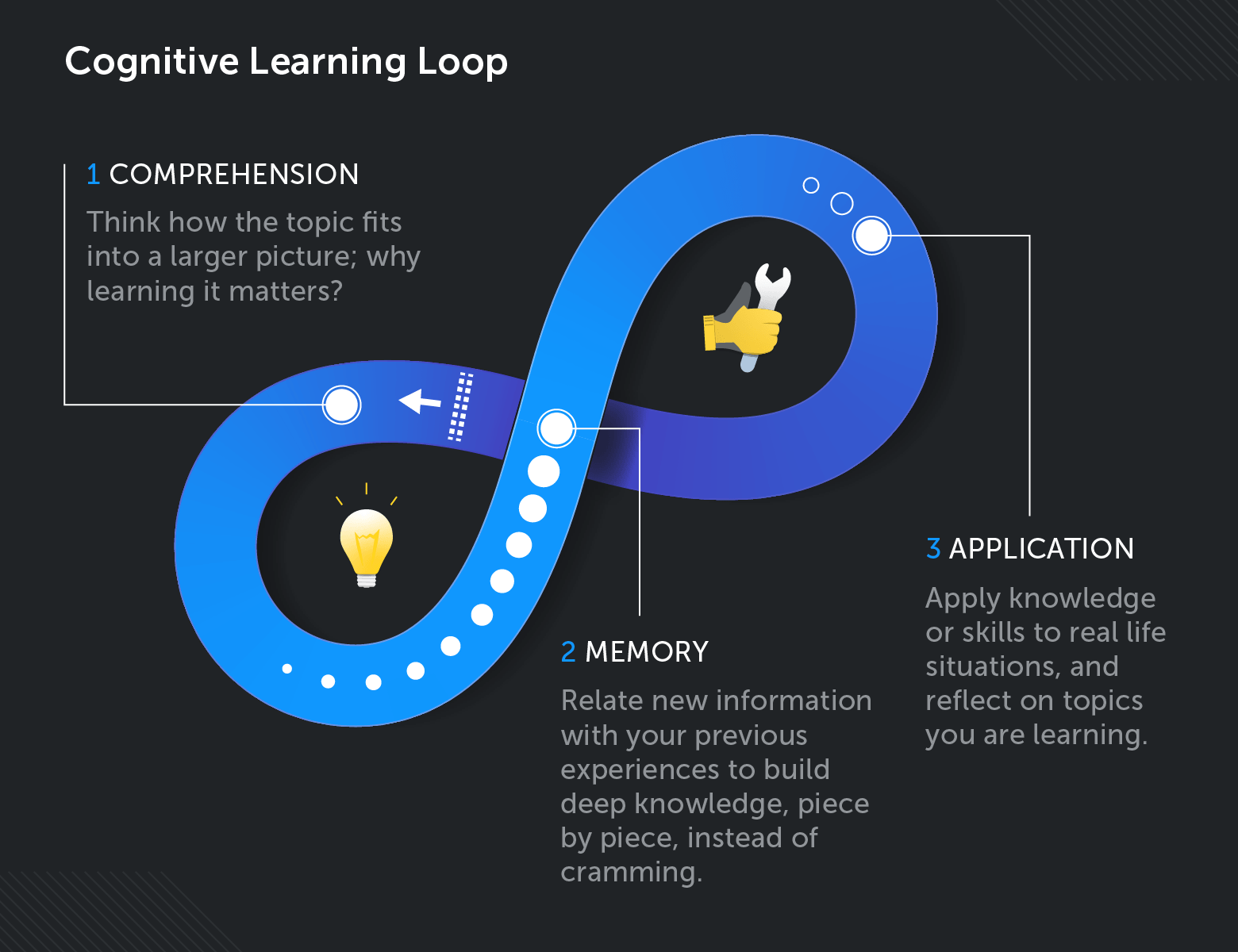
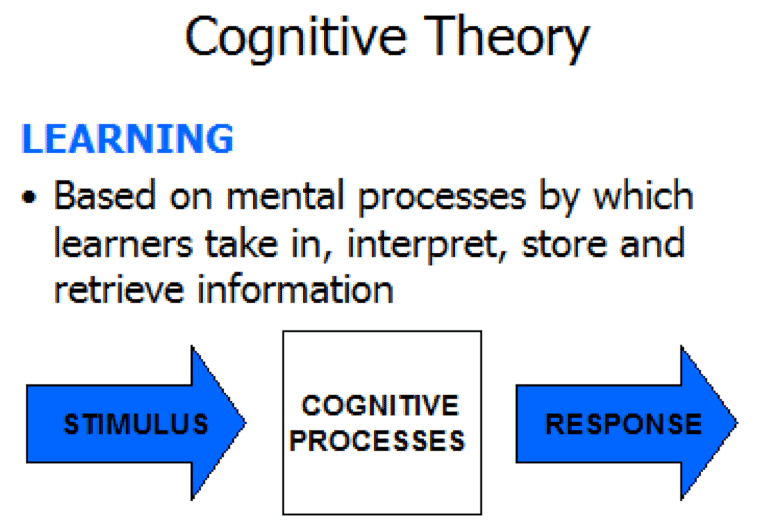
Cognitive Theory Of Learning Definition - Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). This definition has three components: Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how a person receives, organizes, stores and retrieves information. Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts on learning while behavioral cognitive theory explores the impact of.
Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts on learning while behavioral cognitive theory explores the impact of. This definition has three components: Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how a person receives, organizes, stores and retrieves information. Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011).
What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). This definition has three components: Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts on learning while behavioral cognitive theory explores the impact of. Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how a person receives, organizes, stores and retrieves information.
29 Cognitive Learning Examples (2024)
What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Cognitive learning is a change in.
Cognitive Learning Theory Benefits, Strategies and Examples
Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts on learning while behavioral cognitive theory explores the impact of. This definition has three components: Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Cognitive learning is a.
PPT LEARNING THEORIES PRESENTATION PowerPoint Presentation, free
Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. This definition has three components: Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts.
AP Psychology Study Resource Cognitive Learning AP Psychology Community
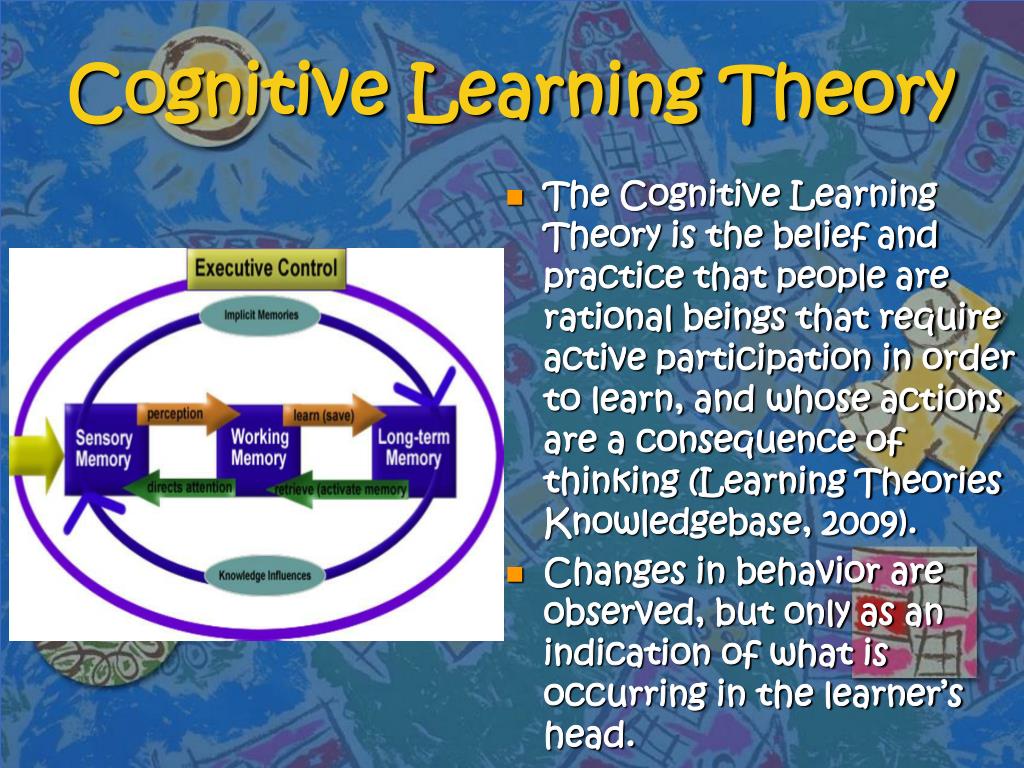
Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how a person receives, organizes, stores and retrieves information. What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts on learning while behavioral cognitive theory explores the impact of. Cognitive load theory, developed by.
Premium Vector Cognitive learning theory educational psychology
This definition has three components: Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts on learning while behavioral cognitive theory explores the impact of. Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of.
Cognitive Learning Theory Definition & Examples University of Phoenix
This definition has three components: Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how a person receives, organizes, stores and retrieves information. What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of.
Cognitive (1)
Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer.
Cognitive learning theory benefits and examples
This definition has three components: Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how a person receives, organizes, stores and retrieves information. Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts.
PPT Learning Theories PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4295003
Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. What is cognitive learning theory? Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). Social cognitive theory focuses on both internal and external impacts on learning while behavioral cognitive theory explores the impact of. Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how.
What is the cognitive learning theory? Benefits and examples
Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people. Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of. This definition has three components: What is cognitive learning theory?
What Is Cognitive Learning Theory?
Cognitive learning theory is defined as a theoretical approach that focuses on how individuals acquire knowledge and develop. This definition has three components: Cognitivism, as a learning theory, reflects how a person receives, organizes, stores and retrieves information. Cognitive load theory, developed by john sweller, suggests that learning is influenced by the amount of.
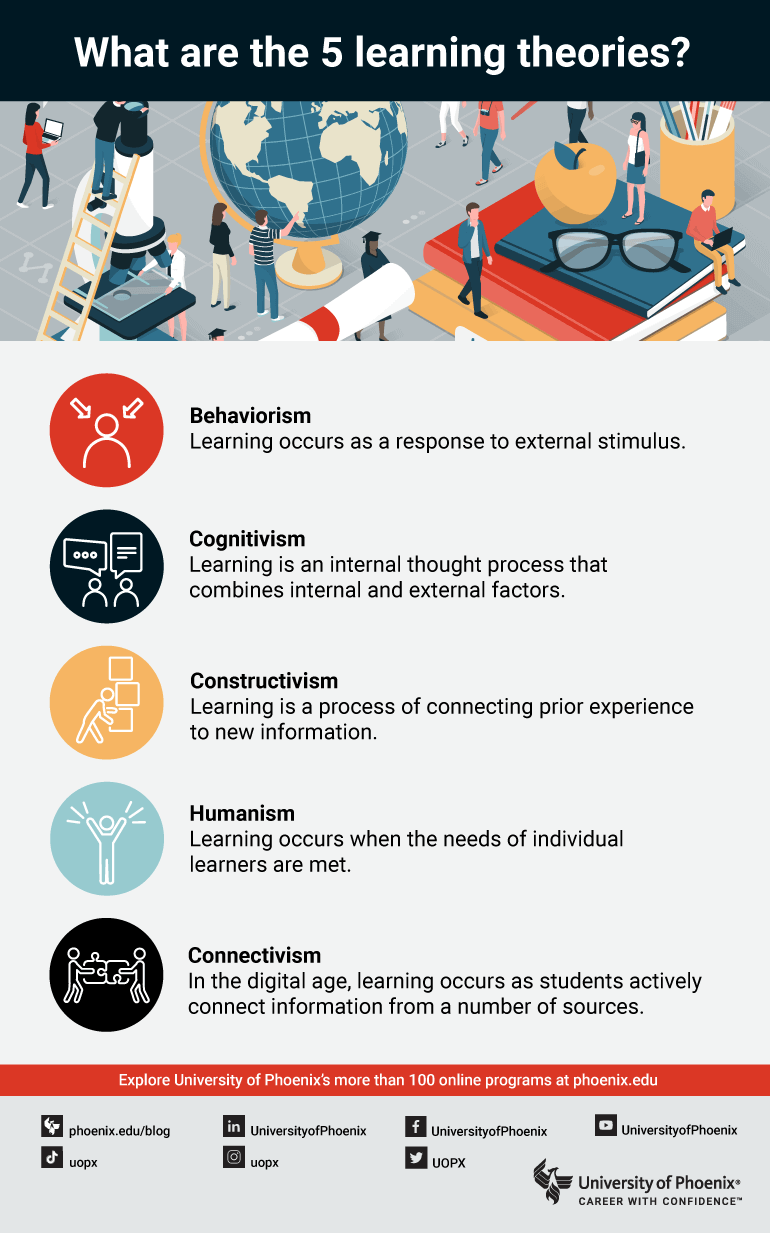
Social Cognitive Theory Focuses On Both Internal And External Impacts On Learning While Behavioral Cognitive Theory Explores The Impact Of.
Cognitive learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience (mayer 2011). Cognitive learning theory uses a process called metacognition to put a focus on how people.