Exposure To Viral Meningitis During Pregnancy
Exposure To Viral Meningitis During Pregnancy - Rubella can be spread by coughing and sneezing. If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus. Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during gestation (congenital. Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. We review some of the outcomes of infection during pregnancy, such as preterm birth, chorioamnionitis, meningitis, hydrocephaly,. You can read the full text of this article if you: Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. Coming in contact with someone with viral meningitis may result in you contracting the virus, but it is unlikely you will develop. For general fact sheets on hfmd,. Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections.
Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. Coming in contact with someone with viral meningitis may result in you contracting the virus, but it is unlikely you will develop. Rubella can be spread by coughing and sneezing. Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. For general fact sheets on hfmd,. We review some of the outcomes of infection during pregnancy, such as preterm birth, chorioamnionitis, meningitis, hydrocephaly,. You can read the full text of this article if you: If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus. Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during gestation (congenital.
Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. We review some of the outcomes of infection during pregnancy, such as preterm birth, chorioamnionitis, meningitis, hydrocephaly,. Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. Coming in contact with someone with viral meningitis may result in you contracting the virus, but it is unlikely you will develop. Rubella can be spread by coughing and sneezing. Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during gestation (congenital. For general fact sheets on hfmd,. You can read the full text of this article if you: If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus.
Meningitis in babies Symptoms and treatment
Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during gestation (congenital. Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Rubella can be spread by coughing and sneezing. For general fact sheets on hfmd,.
Aseptic and Bacterial Meningitis Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention
Coming in contact with someone with viral meningitis may result in you contracting the virus, but it is unlikely you will develop. For general fact sheets on hfmd,. Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Some maternal infections, contracted before or.
VIRAL MENINGITIS CASE STUDY A LOOK INTO VIRAL MENINGITIS
Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus. Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. We review some of the outcomes of infection during pregnancy, such as.
Meningitis
For general fact sheets on hfmd,. Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. You can read the full text of this article if you: Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus.
Meningitis and Pregnancy Lone Star Neurology
Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during gestation (congenital. You can read the full text of this article if you: Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or.
PregnancyRelated Tuberculous Meningitis and Immune Reconstitution
If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus. Rubella can be spread by coughing and sneezing. Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. We review some of the outcomes of infection during pregnancy, such as preterm birth, chorioamnionitis, meningitis, hydrocephaly,. Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral.
PregnancyRelated Tuberculous Meningitis and Immune Reconstitution
For general fact sheets on hfmd,. You can read the full text of this article if you: Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. Coming in contact with someone with viral meningitis may result in you contracting the virus, but it is unlikely you will develop. Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at.
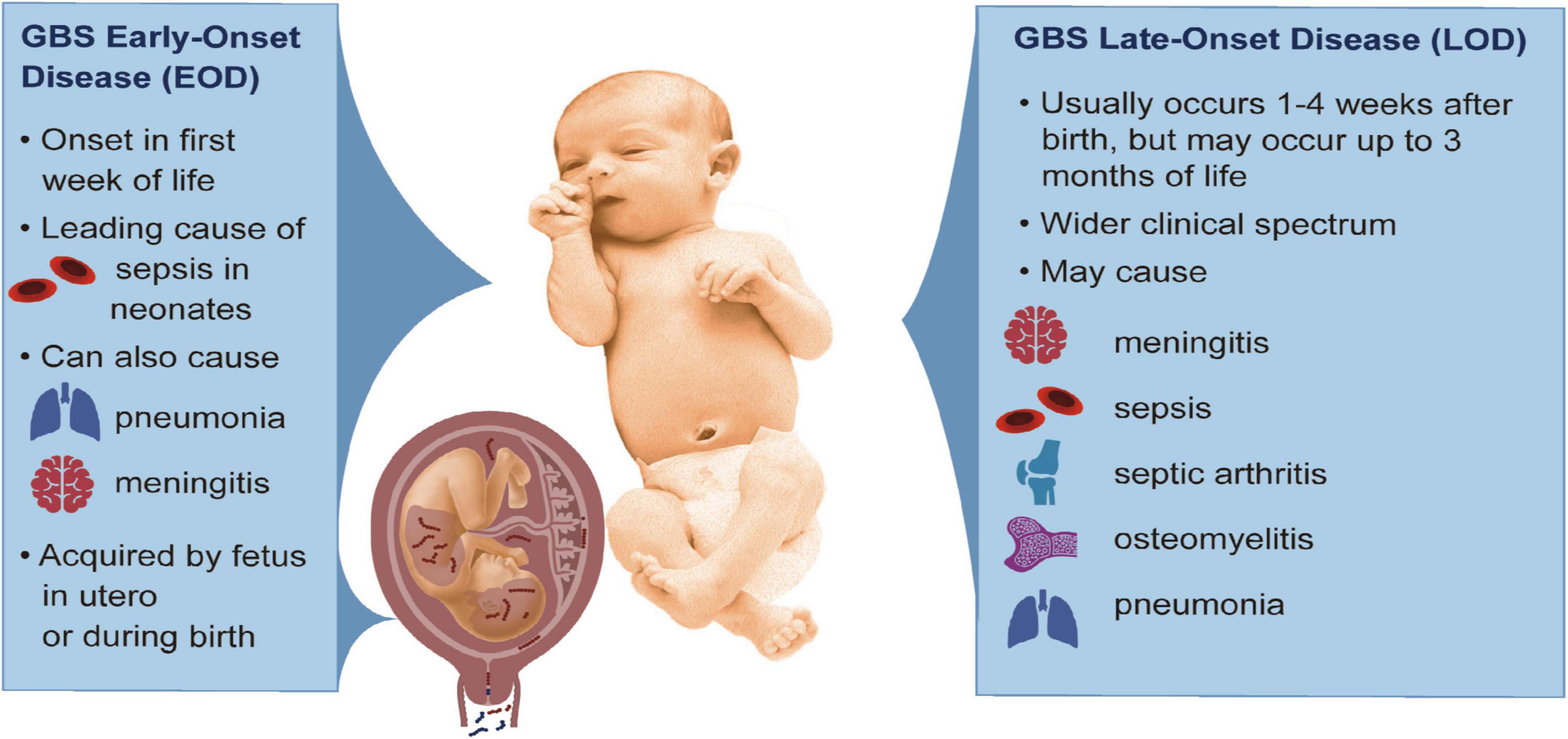
Frontiers Bacterial and Host Determinants of Group B Streptococcal
You can read the full text of this article if you: Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during gestation (congenital. Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. Rubella can be spread by coughing and sneezing. If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus.
Meningococcal Disease (Meningitis) RPH
Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. You can read the full text of this article if you: Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. If someone has rubella during pregnancy, it can be passed to the developing fetus. For general fact sheets on hfmd,.
What are the Causes and Symptoms of Meningitis?
Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. You can read the full text of this article if you: Coming in contact with someone with viral meningitis may result in you contracting the virus, but it is unlikely you will develop. Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during.
If Someone Has Rubella During Pregnancy, It Can Be Passed To The Developing Fetus.
Meningitis presenting as dysarthria and otalgia at 28. Coming in contact with someone with viral meningitis may result in you contracting the virus, but it is unlikely you will develop. Some maternal infections, contracted before or during pregnancy, can be transmitted to the fetus, during gestation (congenital. For general fact sheets on hfmd,.
You Can Read The Full Text Of This Article If You:
Rubella can be spread by coughing and sneezing. Rarely, patients with coxsackievirus a16 or enterovirus 71 (ev71) infections may develop viral meningitis. Meningitis during pregnancy can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. We review some of the outcomes of infection during pregnancy, such as preterm birth, chorioamnionitis, meningitis, hydrocephaly,.