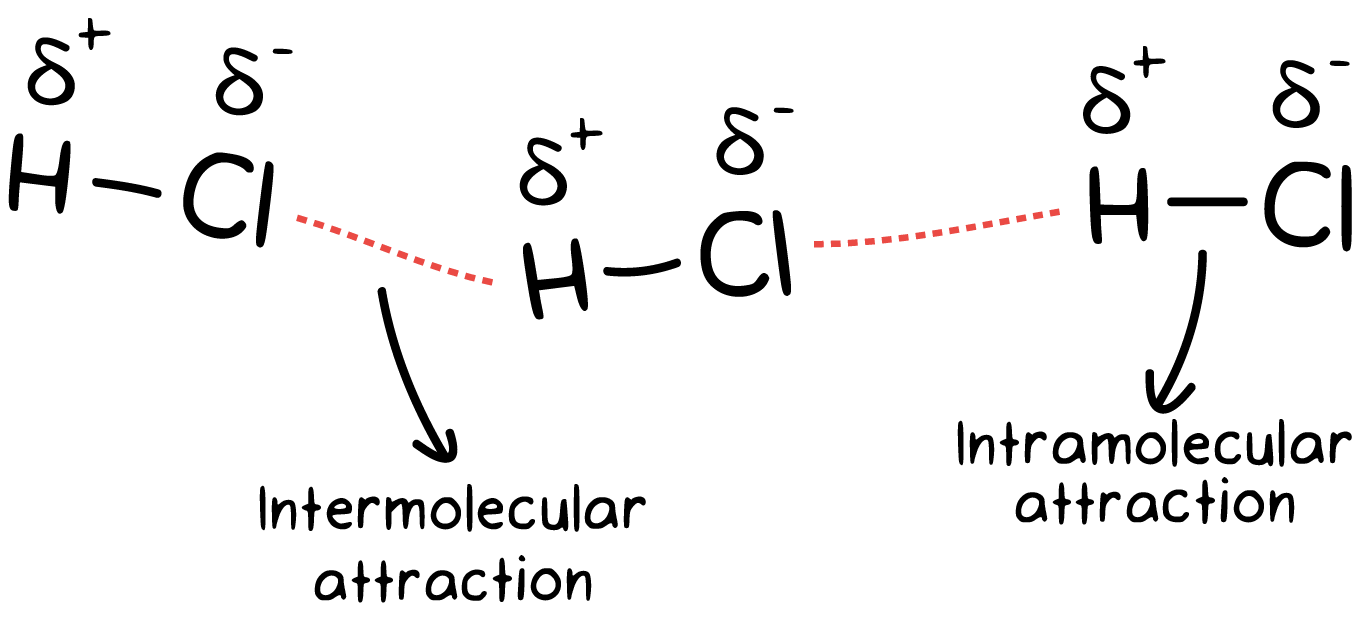
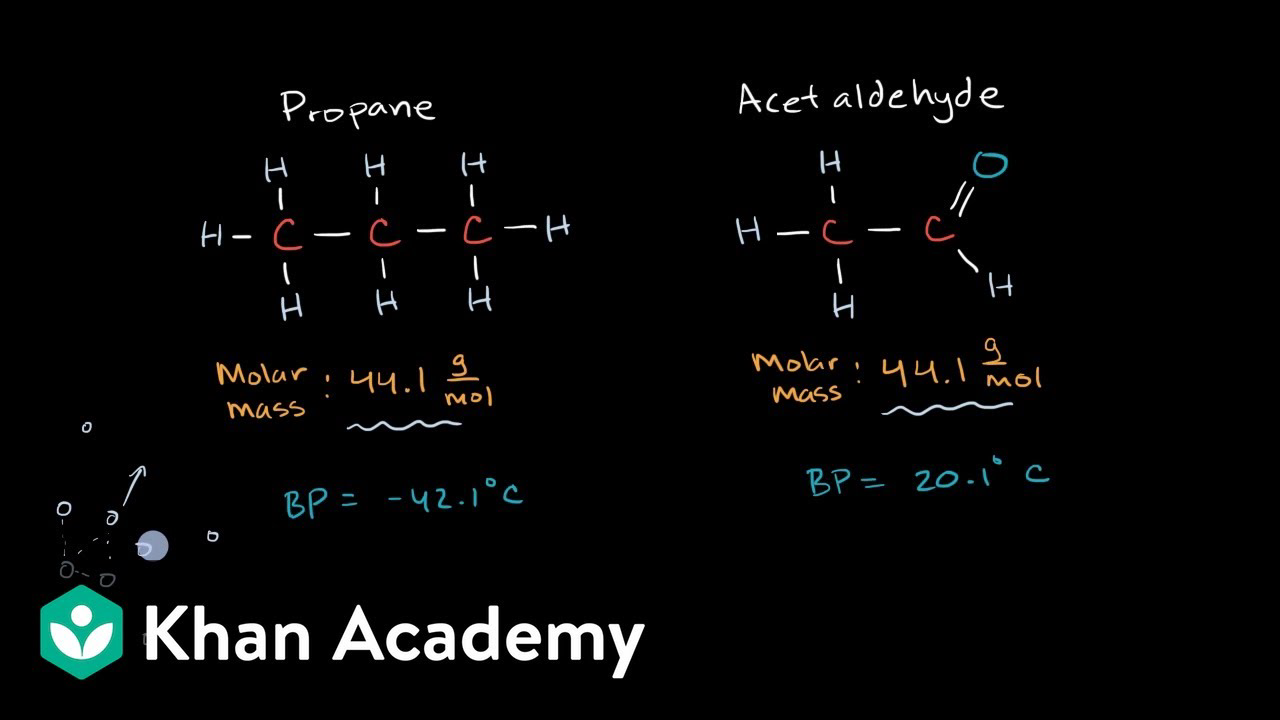
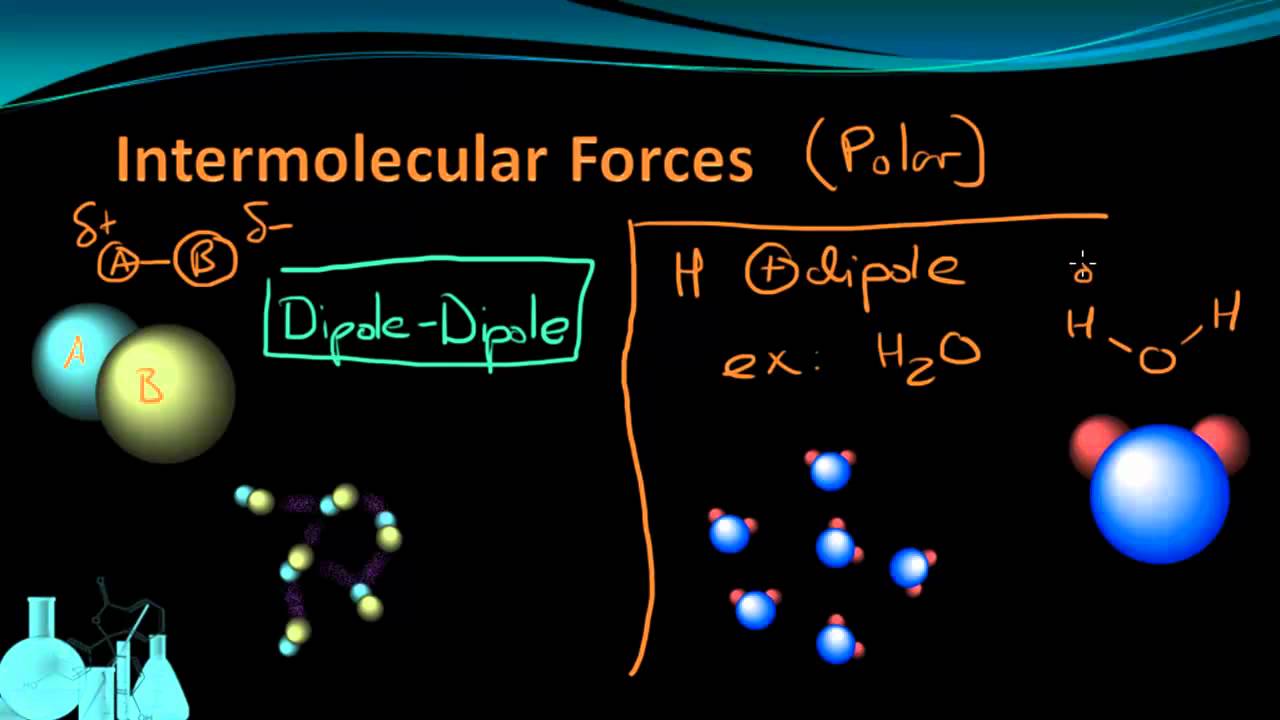
Intermolecular Forces Khan Academy
Intermolecular Forces Khan Academy - Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. The stronger these forces, the lower. Nonpolar substances are generally more.
A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. Nonpolar substances are generally more. The stronger these forces, the lower. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like).
Nonpolar substances are generally more. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. The stronger these forces, the lower.
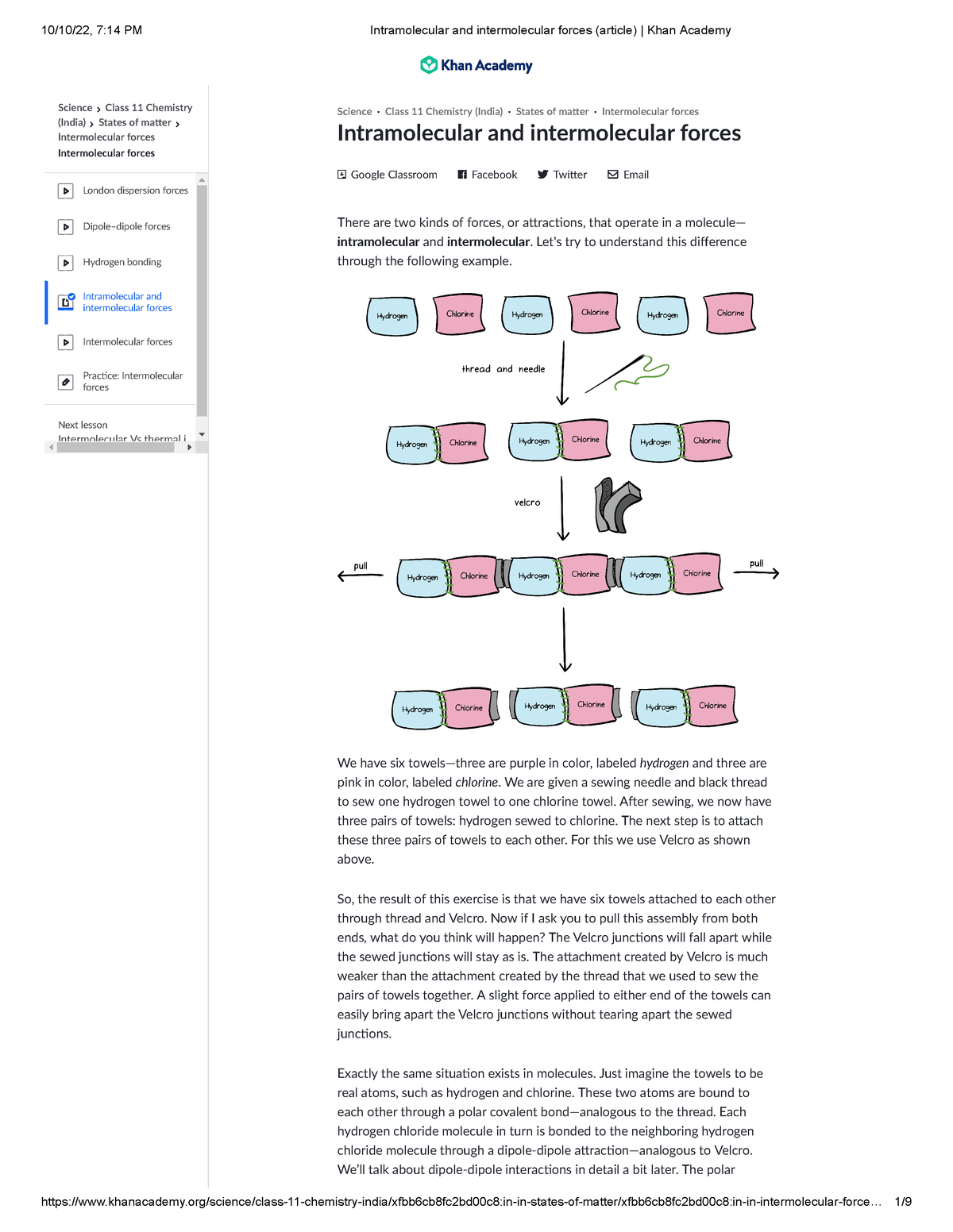
Intramolecular and intermolecular forces (article) Khan Academy
Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. The stronger these forces, the lower. Nonpolar substances are generally more.
H2S Intermolecular Forces (Strong or Weak) Techiescientist
The stronger these forces, the lower. A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). Nonpolar substances are generally more.
Intermolecular Forces in Chemistry
A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. Nonpolar substances are generally more. The stronger these forces, the lower. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like).
Intramolecular and intermolecular forces (article) Khan Academy in
Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). Nonpolar substances are generally more. The stronger these forces, the lower. A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules.
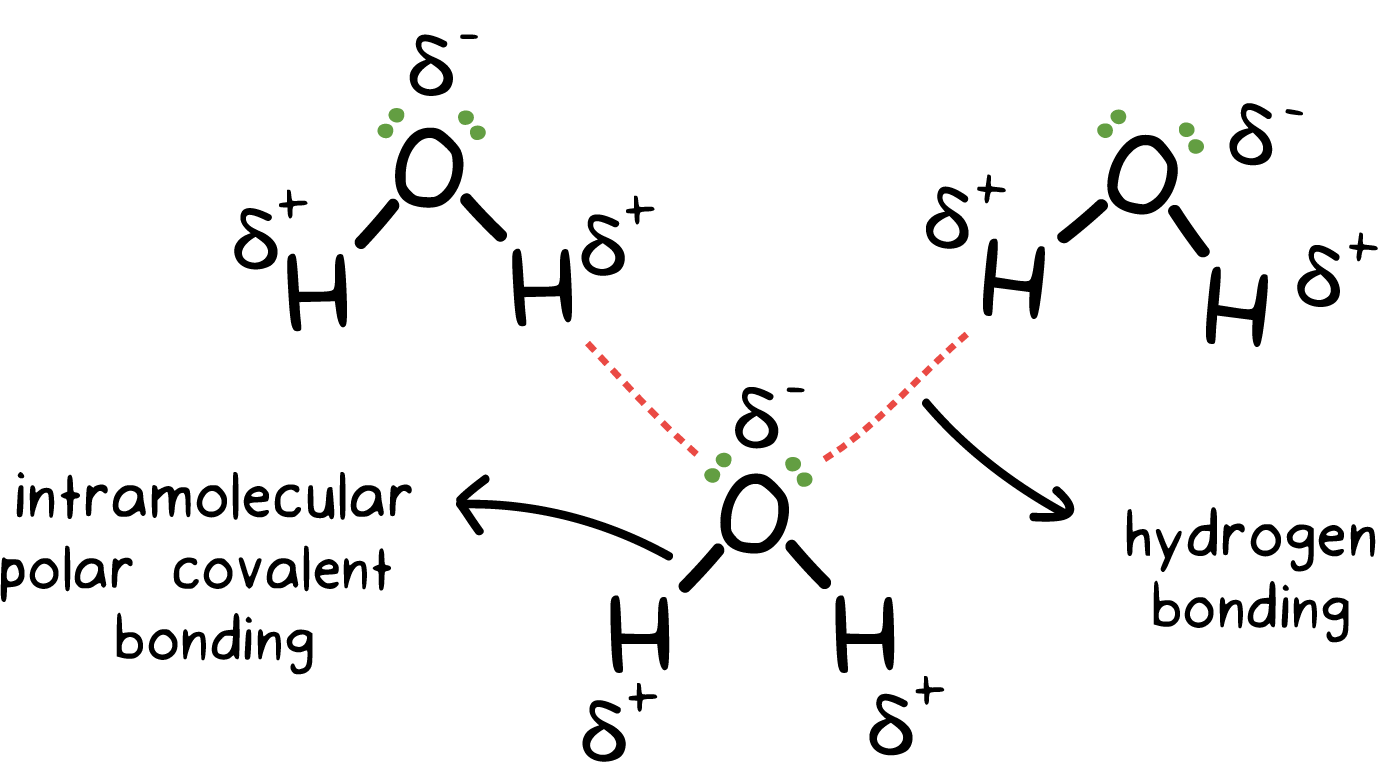
[DIAGRAM] Ch3och3 Intermolecular Forces Diagram
Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). Nonpolar substances are generally more. The stronger these forces, the lower. A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules.
CH4 Intermolecular Forces Techiescientist
A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. The stronger these forces, the lower. Nonpolar substances are generally more. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like).
Fillable Online Intramolecular and intermolecular forces (article)Khan
A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. The stronger these forces, the lower. Nonpolar substances are generally more. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like).
Intermolecular forces (apply) (practice) Khan Academy
Nonpolar substances are generally more. A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). The stronger these forces, the lower.
Chemistry 4.9 Intermolecular Forces YouTube
A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules. Nonpolar substances are generally more. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). The stronger these forces, the lower.
Intramolecular vs Intermolecular Forces YouTube
Nonpolar substances are generally more. Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). The stronger these forces, the lower. A liquid’s vapor pressure is directly related to the intermolecular forces present between its molecules.
A Liquid’s Vapor Pressure Is Directly Related To The Intermolecular Forces Present Between Its Molecules.
Substances with similar polarities tend to be soluble in one another (like dissolves like). Nonpolar substances are generally more. The stronger these forces, the lower.


![[DIAGRAM] Ch3och3 Intermolecular Forces Diagram](http://clipart-library.com/img1/1419819.png)