Molecular Orbital Theory Khan Academy
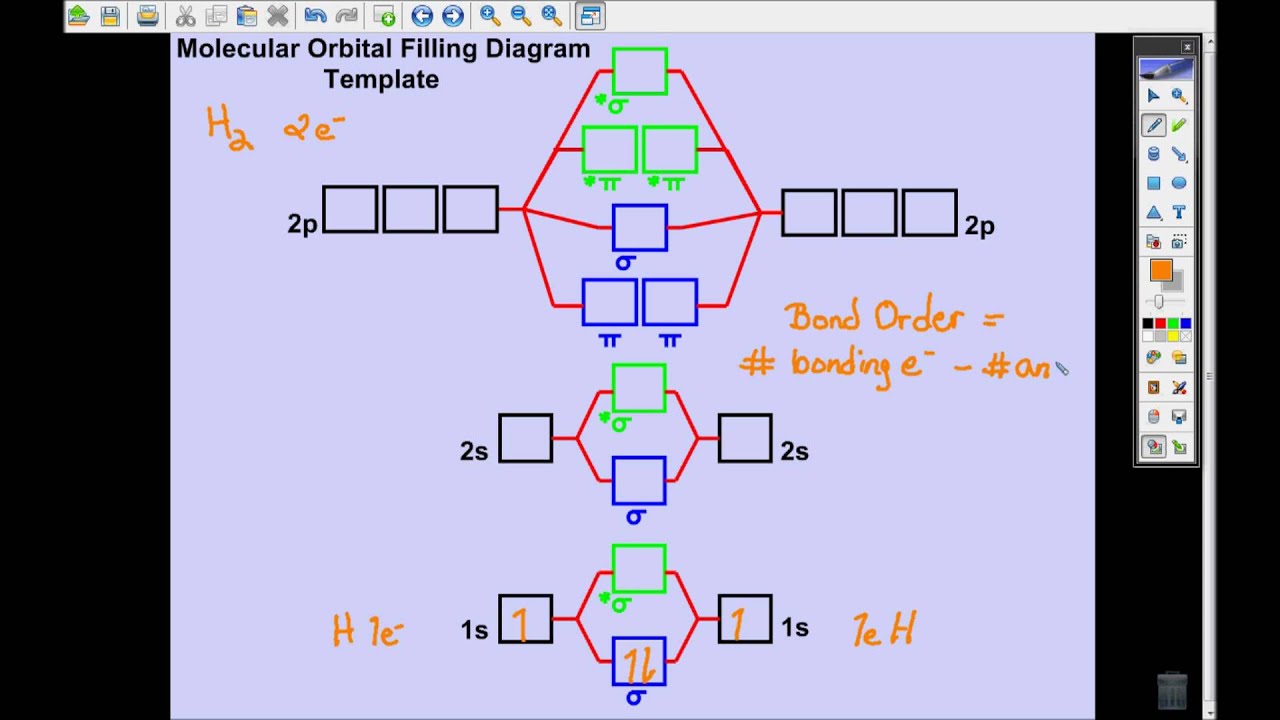
Molecular Orbital Theory Khan Academy - Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital theory and chemical bonding. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. If you're behind a web filter, please. When a nitrogen atom forms an ammonia. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals. It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of atomic orbitals.
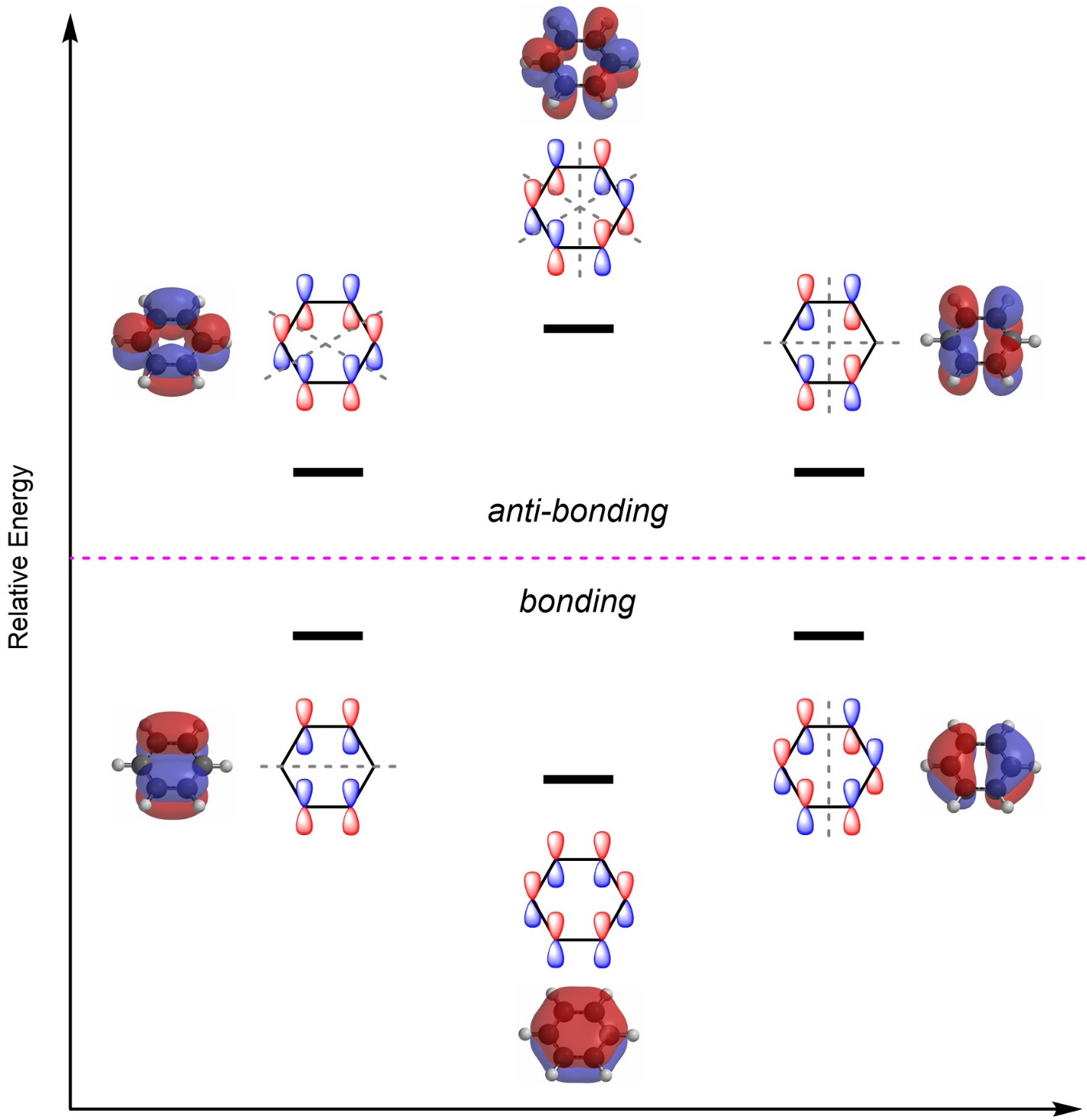
It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of atomic orbitals. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals. When a nitrogen atom forms an ammonia. This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital theory and chemical bonding. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy. This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. If you're behind a web filter, please.
Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy. It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of atomic orbitals. This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. When a nitrogen atom forms an ammonia. This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital theory and chemical bonding. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals. If you're behind a web filter, please.
SOLUTION Molecular orbital theory Studypool
This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital theory and chemical bonding. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having.
merkez dağıtım kılıç bo molecular orbital diagram Merkez Sinis söndürmek
This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please. Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Khan Academy Hanenhuusholli
It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of atomic orbitals. Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. When a nitrogen atom forms an ammonia.
9.1. (Very) Brief Discussion on the Uses of Molecular Orbital Theory
When a nitrogen atom forms an ammonia. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Explore advanced applications of.
SOLUTION Molecular orbital theory Studypool
This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital theory and chemical bonding. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Khan Academy Hanenhuusholli
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence. This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Theory, Part 2 YouTube
It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of atomic orbitals. Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of.
The Complete Guide to Understanding Molecular Orbital Diagrams on Khan
If you're behind a web filter, please. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. When a nitrogen atom forms an ammonia. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals. This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital.
Understanding Molecular Orbital Diagrams A Khan Academy Guide
If you're behind a web filter, please. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence. Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy..
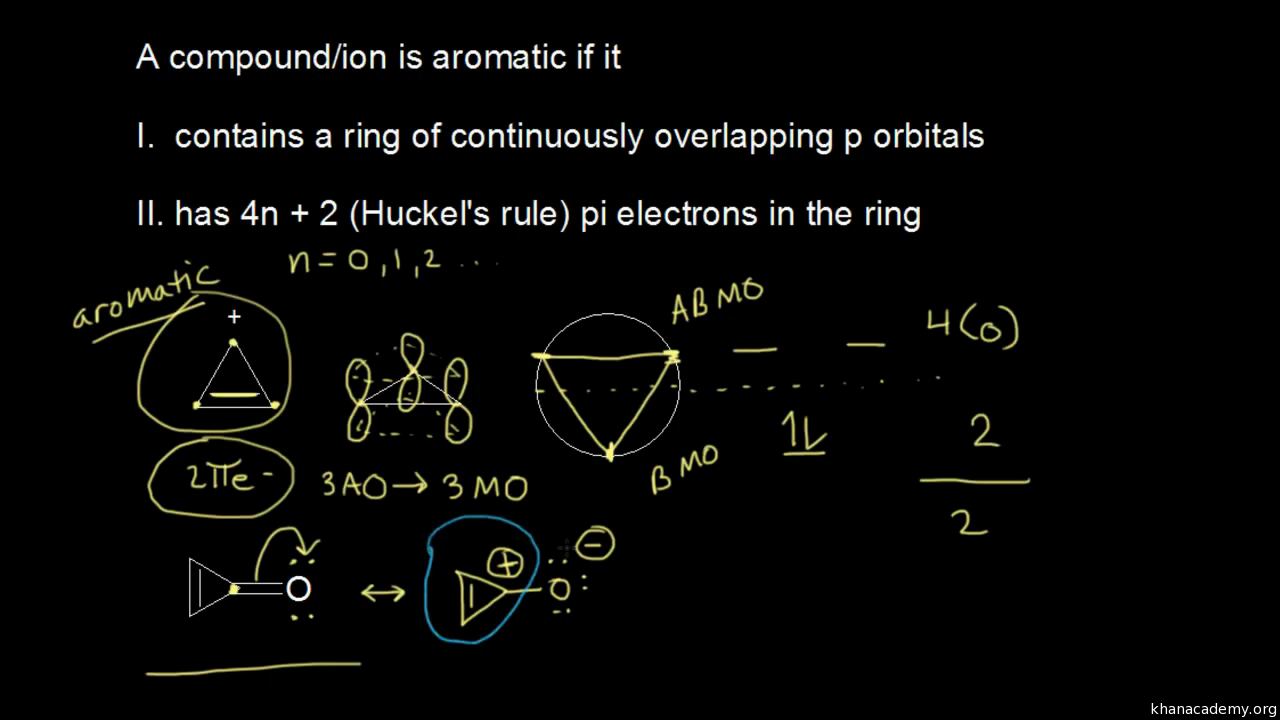
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) → molecular orbital theory explains abou..
It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of atomic orbitals. Explore advanced applications of molecular orbital theory in this comprehensive guide on khan academy. This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital theory and chemical bonding. This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. In molecular orbital.
Explore Advanced Applications Of Molecular Orbital Theory In This Comprehensive Guide On Khan Academy.
This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. This is a great question that goes into the details of molecular orbital theory and chemical bonding. If you're behind a web filter, please. In mo theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals.
When A Nitrogen Atom Forms An Ammonia.
It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of atomic orbitals. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.