Second Normal Form
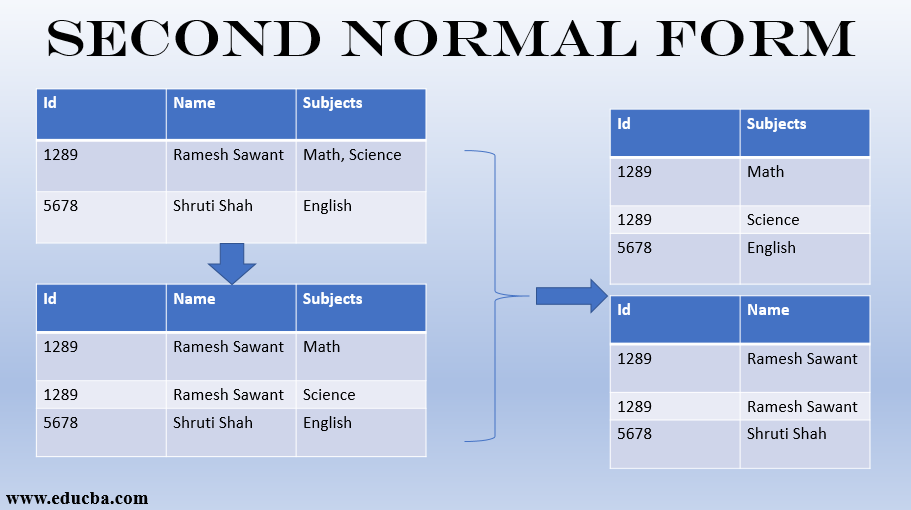
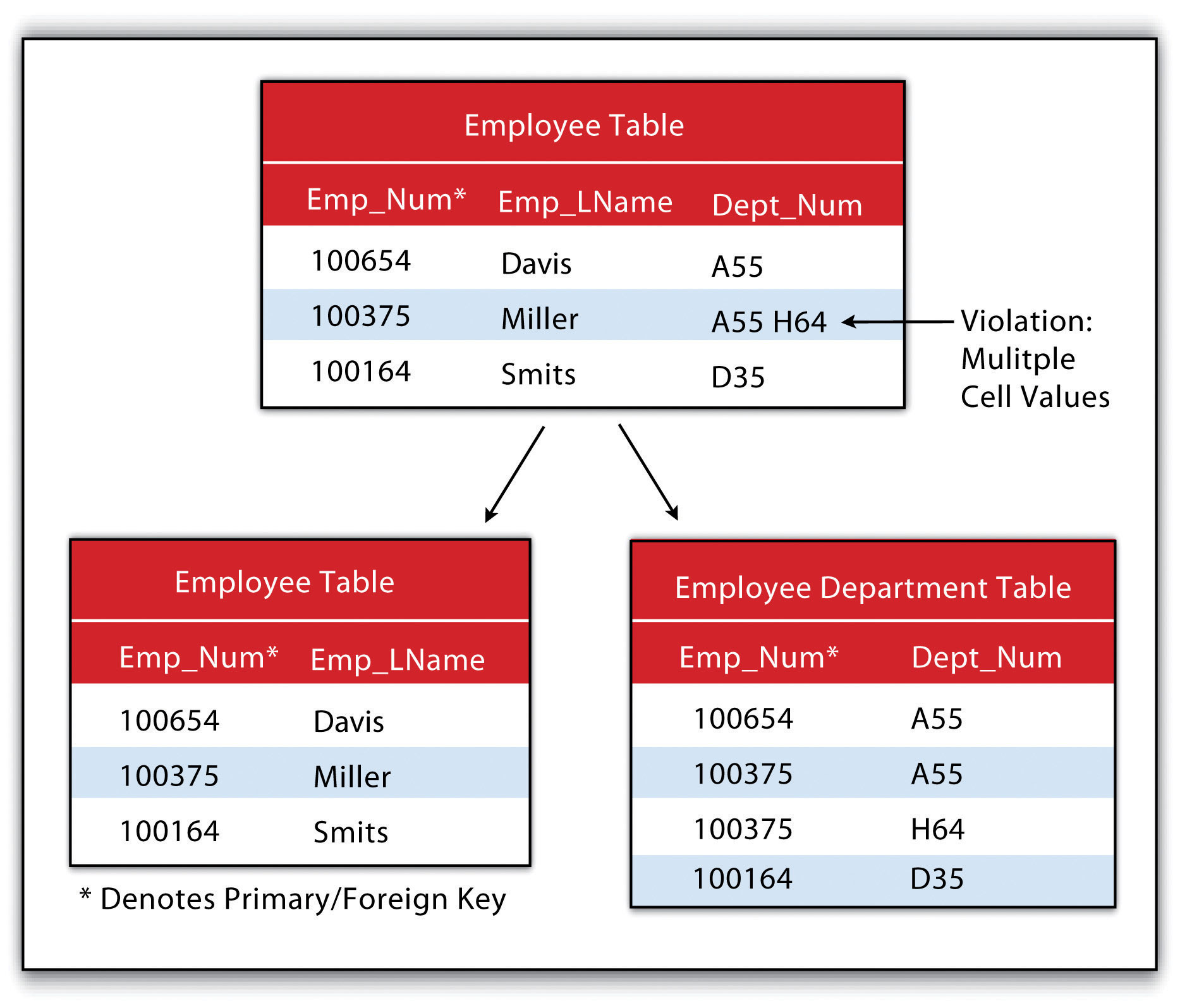
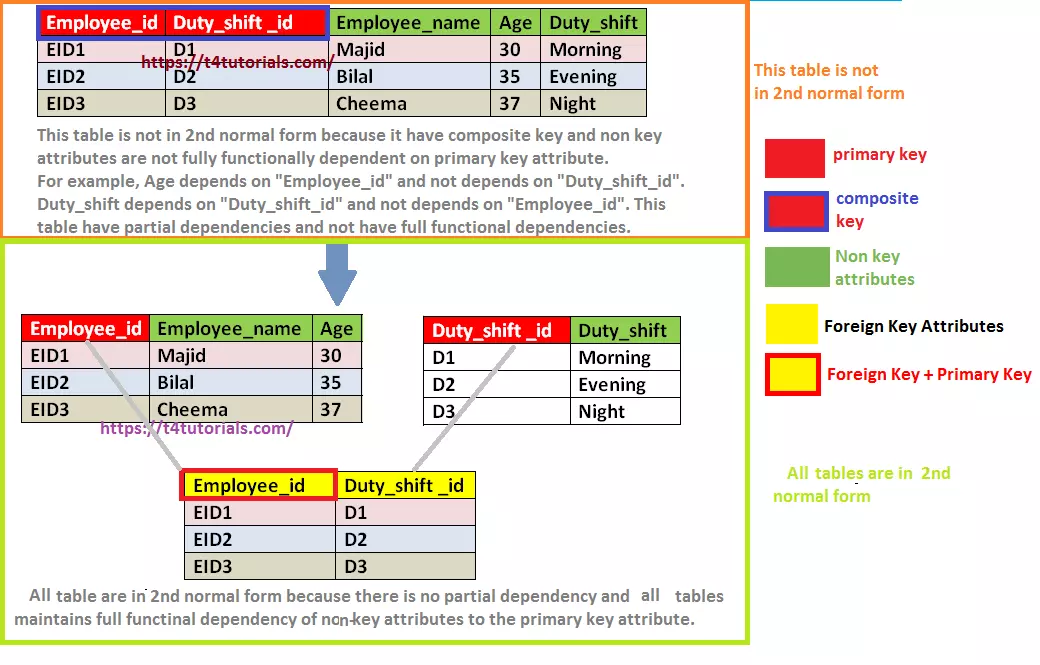
Second Normal Form - A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the data is in 2nf if following conditions are completed by data : It is in first normal form. Let's assume, a school can. The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more attributes. Second normal form (2nf), in database normalization, is a normal form. A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements: Second normal form (2nf) in the 2nf, relational must be in 1nf. The 1nf only eliminates repeating groups, not redundancy.
The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more attributes. The 1nf only eliminates repeating groups, not redundancy. That’s why there is 2nf. Second normal form (2nf) in the 2nf, relational must be in 1nf. A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) It is in first normal form. Let's assume, a school can. In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the data is in 2nf if following conditions are completed by data : A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements:
Let's assume, a school can. 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: Second normal form (2nf), in database normalization, is a normal form. Second normal form (2nf) in the 2nf, relational must be in 1nf. It is in first normal form. The 1nf only eliminates repeating groups, not redundancy. In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the data is in 2nf if following conditions are completed by data : The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more attributes. A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements:
Second Normal Form
That’s why there is 2nf. The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more attributes. Second normal form (2nf) in the 2nf, relational must be in 1nf. A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements: 1.the data should be in.
PPT Normalization of Tables PowerPoint Presentation ID458641
That’s why there is 2nf. 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements: The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more attributes. The 1nf only eliminates repeating groups, not.
2_4 Second Normal Form YouTube
The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more attributes. 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) That’s why there is 2nf. Let's assume, a school can. Second normal form (2nf), in database normalization, is a normal form.
Second Normal Form Brief Overview of Second Normal Form
A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) That’s why there is 2nf. Let's assume, a school can. Second normal form (2nf) in the 2nf, relational must be in 1nf.
Geospatial Data Management
Let's assume, a school can. Second normal form (2nf), in database normalization, is a normal form. A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) It is in first normal form.
Second Normal Form (2NF) Database Normalization DBMS YouTube
1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) The 1nf only eliminates repeating groups, not redundancy. A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the data is in 2nf if following conditions are completed by data :.
Second Normal Form In DBMS 2nd Normal Form In Dbms2nf In DBMSSecond
Let's assume, a school can. A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements: Second normal form (2nf) in the 2nf, relational must be in 1nf. It is in first normal form. The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more.
Second Normal Form (2NF) Database Normalization in Hindi
Let's assume, a school can. A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements: 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the.
PPT Second Normal Form (2NF) PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Second normal form (2nf), in database normalization, is a normal form. In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the data is in 2nf if following conditions are completed by data : 1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) Second normal form (2nf) in the 2nf, relational must be in.
Second normal form Examples in DBMS
The second normal form applies to relations with composite keys, that is, relations with a primary key composed of two or more attributes. In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the data is in 2nf if following conditions are completed by data : Second normal form (2nf), in database normalization, is a.
The Second Normal Form Applies To Relations With Composite Keys, That Is, Relations With A Primary Key Composed Of Two Or More Attributes.
The 1nf only eliminates repeating groups, not redundancy. A table is said to be in 2nf if it meets the following criteria: It is in first normal form. In this section i would like to explain the second normal form with real life examples.the data is in 2nf if following conditions are completed by data :
Second Normal Form (2Nf), In Database Normalization, Is A Normal Form.
1.the data should be in first normal form (1 nf) Let's assume, a school can. A relation is in the second normal form if it fulfills the following two requirements: That’s why there is 2nf.