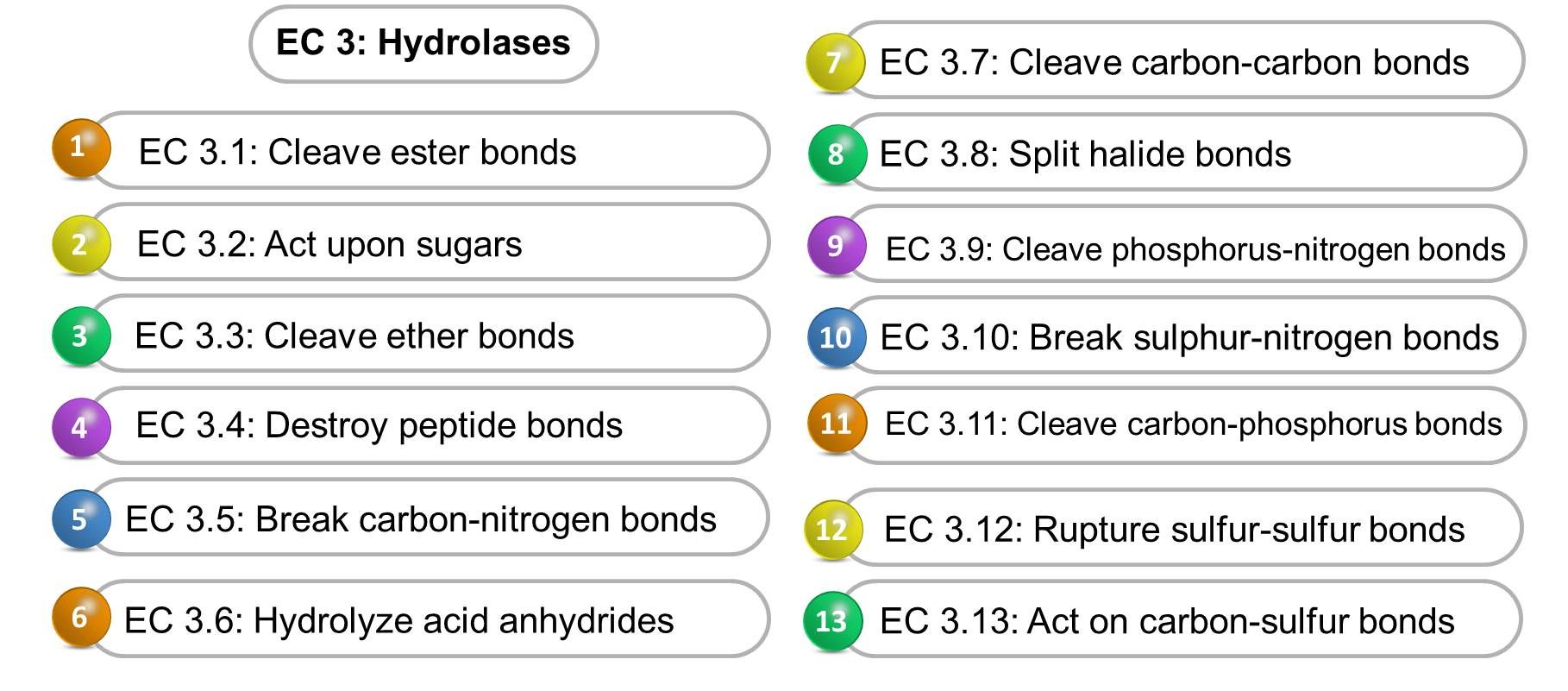
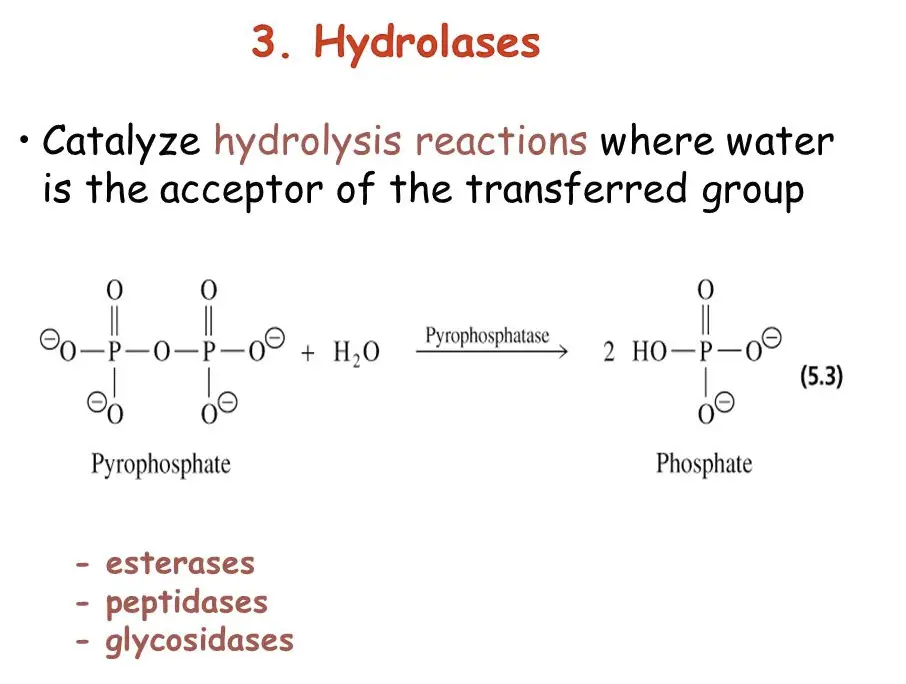
What Are Hydrolases
What Are Hydrolases - Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. The natural function of most hydrolases is. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex.
The natural function of most hydrolases is. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two.
Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. The natural function of most hydrolases is. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules.
Hydrolase Introduction Creative Enzymes
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. In simple words, a.
Expanding the Toolkit for the Serine Hydrolases Chemistry & Biology
Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme.
What are Hydrolase Enzymes? MCAT Biochemistry YouTube
In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme.
Image Tutorial Glycoside Hydrolases
Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. The natural function of most hydrolases is. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins,.
Hydrolases Enzyme Biochemistry
Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water.
Hydrolase Meaning YouTube
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. The natural function of most hydrolases is. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the.
Gels Free FullText Short Peptides for Hydrolase Supramolecular
In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. The natural function of most hydrolases is..
Hydrolase définition et explications
In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules. The natural function of most hydrolases is. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water..
CN Hydrolases
Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large molecule into two. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules..
Difference Between Hydrolase And Transferase Relationship Between
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. The natural function of most hydrolases is. Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. Hydrolases are hydrolytic enzymes that use water to catalyze the cleavage of chemical bonds, usually breaking a large.
Hydrolases Are Hydrolytic Enzymes That Use Water To Catalyze The Cleavage Of Chemical Bonds, Usually Breaking A Large Molecule Into Two.
The natural function of most hydrolases is. In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that speeds up the hydrolysis of proteins, starch, fats, nucleic acids, and other complex. Hydrolases are the group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. In simple words, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond in biomolecules.