What Is Orientation Math
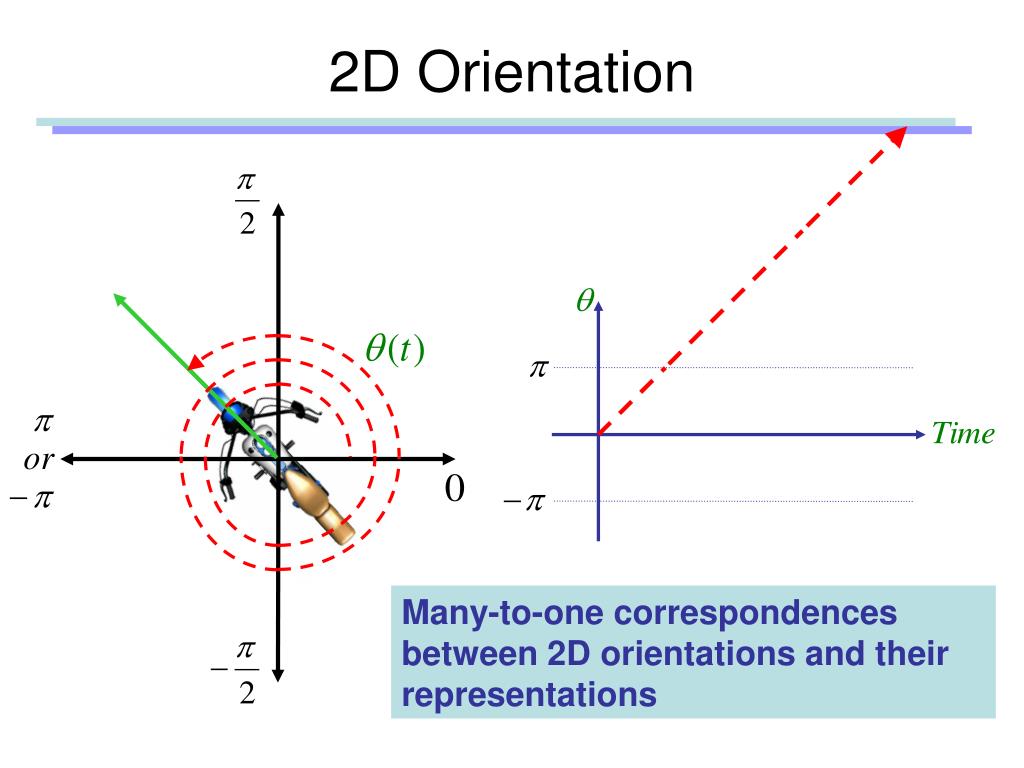
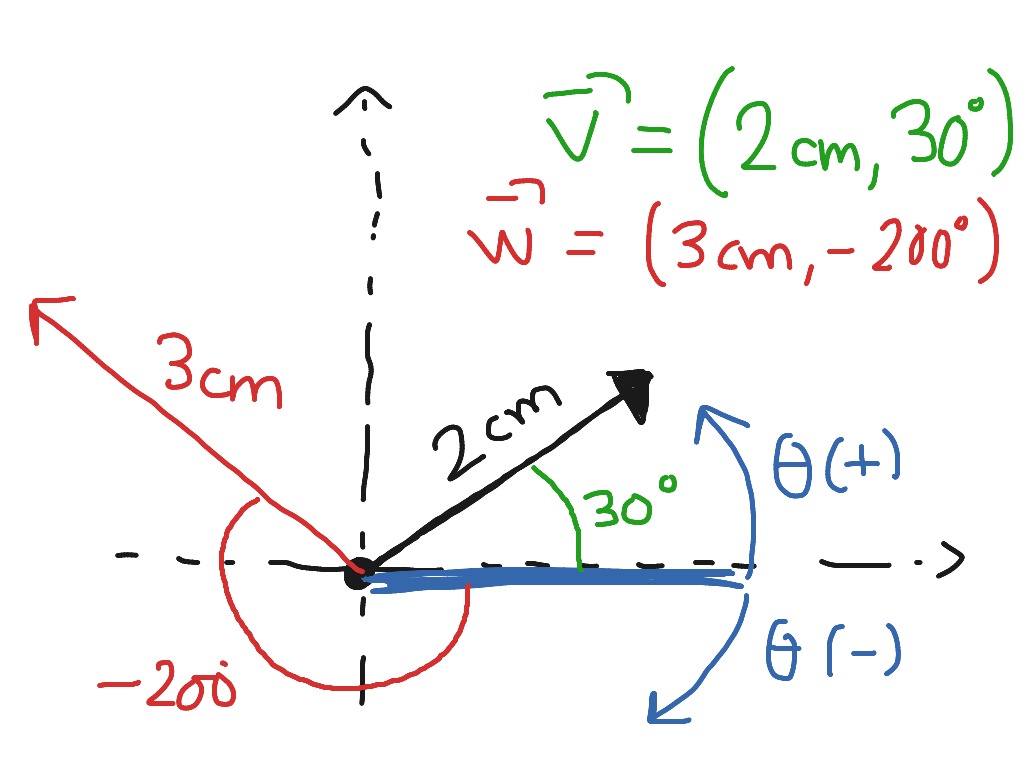
What Is Orientation Math - Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand the. What is orientation in math? An orientation is prescribed by giving an ordered pair of linearly independent vectors. Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis). V = (v1, v2) , w = (w1 , w2). By definition the direction of rotation from v.
An orientation is prescribed by giving an ordered pair of linearly independent vectors. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand the. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. By definition the direction of rotation from v. V = (v1, v2) , w = (w1 , w2). What is orientation in math? Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis). In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and.
By definition the direction of rotation from v. It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand the. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. V = (v1, v2) , w = (w1 , w2). An orientation is prescribed by giving an ordered pair of linearly independent vectors. Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis). Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. What is orientation in math? In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure.
PPT Rotation and Orientation Fundamentals PowerPoint Presentation
Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and. V.
ORIENTATION Virtual Math Abode of Local Media Station NCTV45 "The
V = (v1, v2) , w = (w1 , w2). Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis). Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. An orientation is prescribed by giving an ordered pair of linearly independent vectors..
Orientation (geometry) Wikipedia
Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. By definition the direction of rotation from v. An orientation is prescribed by giving an ordered pair of linearly independent vectors. In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or.
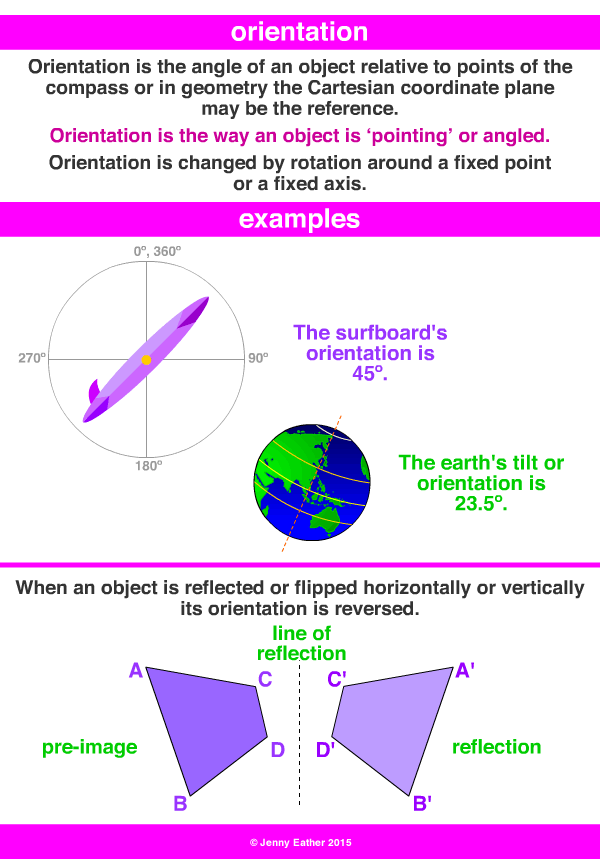
orientation A Maths Dictionary for Kids Quick Reference by Jenny Eather
Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. What is orientation in math? Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. V = (v1, v2) , w = (w1 , w2). By definition the direction of rotation from v.
Orientation (geometry) YouTube
Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and. V.
Vecteursorientationsensdirection Math ShowMe
In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and. Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis). An orientation is prescribed by giving an ordered pair of linearly independent vectors. What is orientation.
Math Orientation YouTube
By definition the direction of rotation from v. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. What is orientation in math? It is a fundamental concept that helps us understand the. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space.
to Orientation Math 62DE
Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis). Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. V = (v1, v2) , w = (w1 , w2). By definition the direction of rotation from v. Orientation in geometry refers to.
PPT Transformational Geometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download
What is orientation in math? Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and. Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of.
NVC Mandatory MATH 1414 Orientation (MATH 0080) Alamo Colleges
In mathematics, orientability is a broader notion that, in two dimensions, allows one to say when a cycle goes around clockwise or counterclockwise, and. Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis). Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. Orientation.
In Mathematics, Orientability Is A Broader Notion That, In Two Dimensions, Allows One To Say When A Cycle Goes Around Clockwise Or Counterclockwise, And.
Orientation, in the context of mathematics, refers to the relative position or direction of an object or shape. Orientation in geometry refers to the direction or placement of objects or shapes in space. An orientation is prescribed by giving an ordered pair of linearly independent vectors. Orientation is specified by the relationship between the vector and given reference lines (which i'm interpreting to be some basis).
It Is A Fundamental Concept That Helps Us Understand The.
What is orientation in math? V = (v1, v2) , w = (w1 , w2). Orientation is the relative arrangements of points after a transformation or after traveling around a geometric figure. By definition the direction of rotation from v.