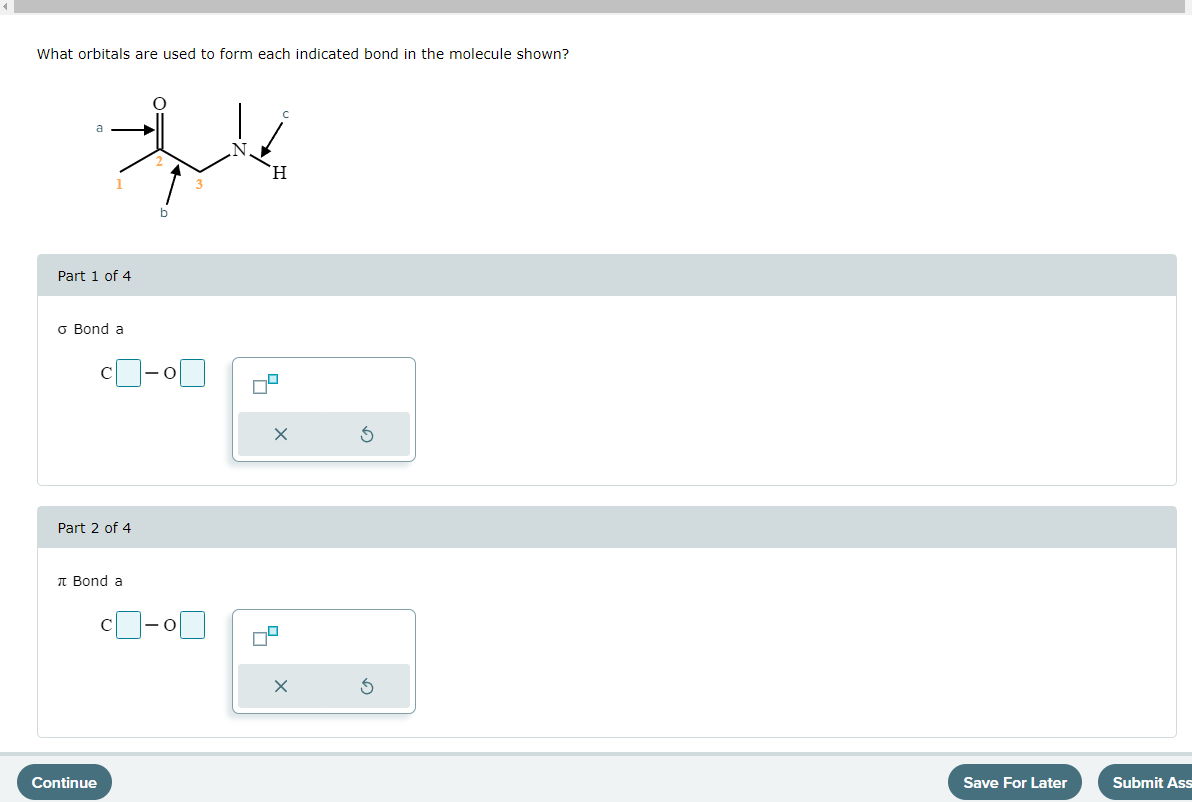
What Orbitals Are Used To Form The Indicated Bond
What Orbitals Are Used To Form The Indicated Bond - Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two.
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two.
In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two.
What Orbitals Are Used To Form The Bond Indicated In The Following
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two.
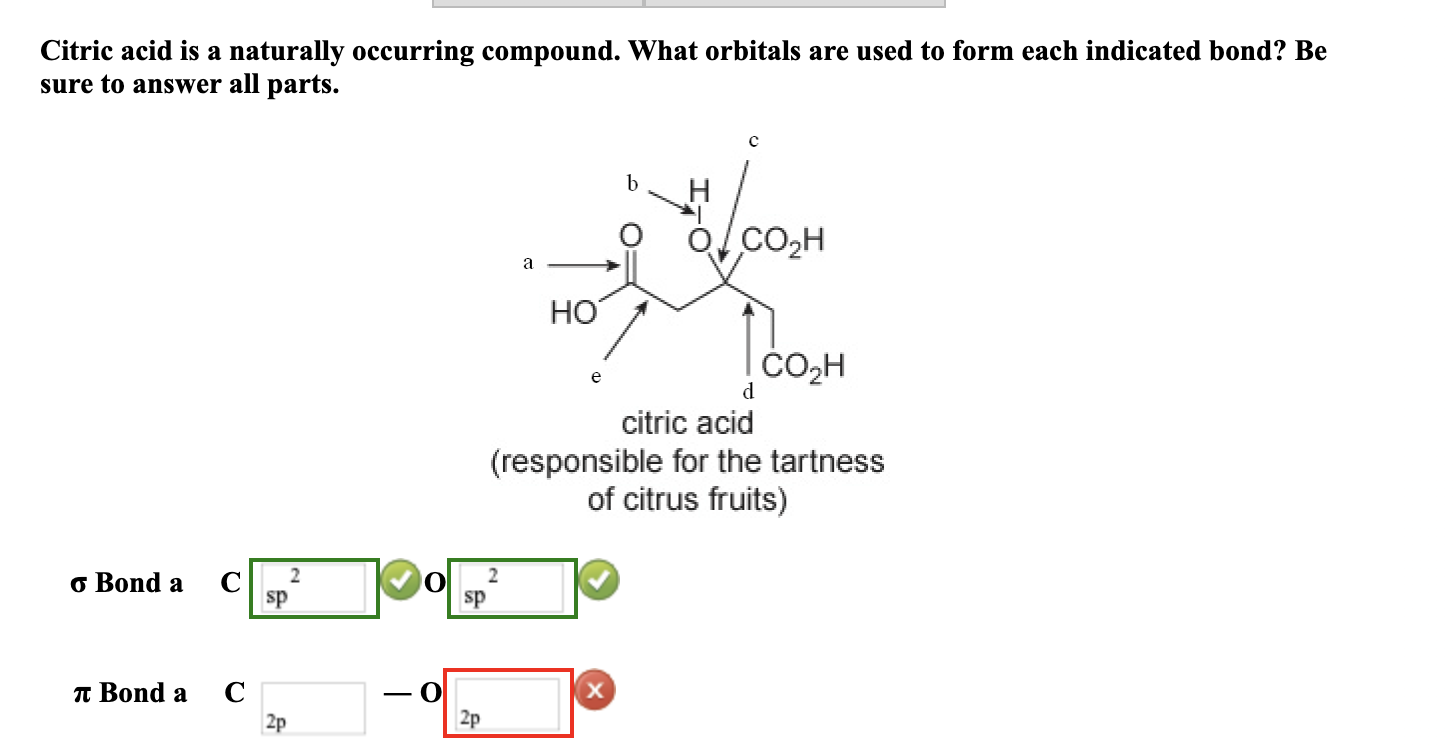
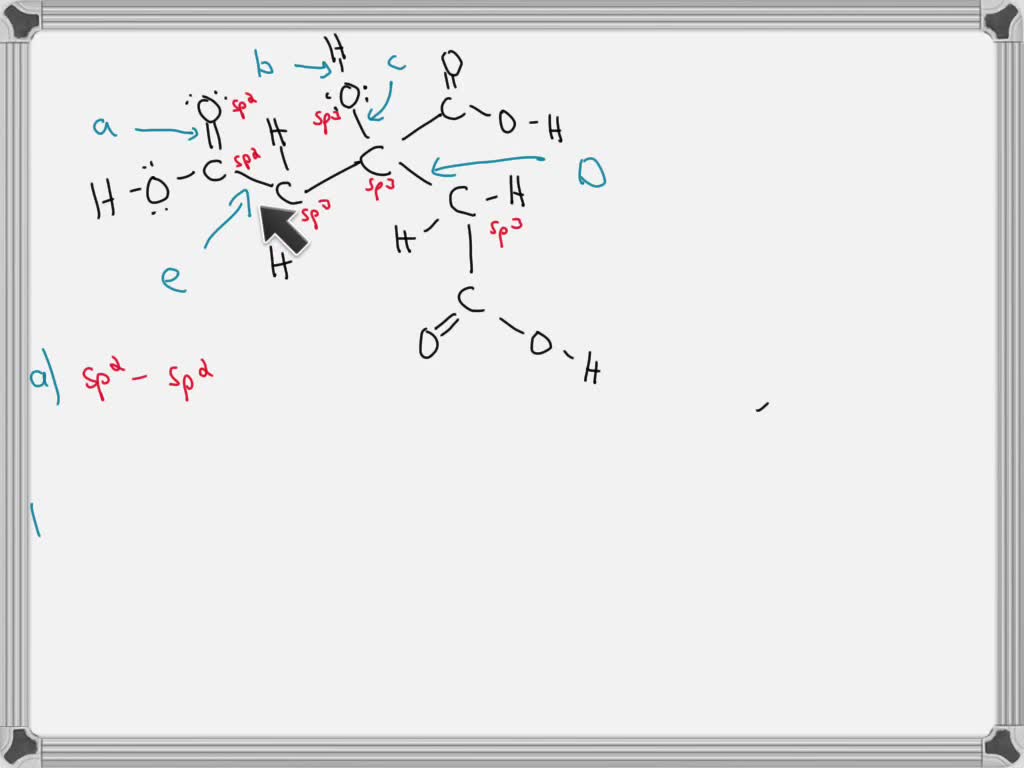
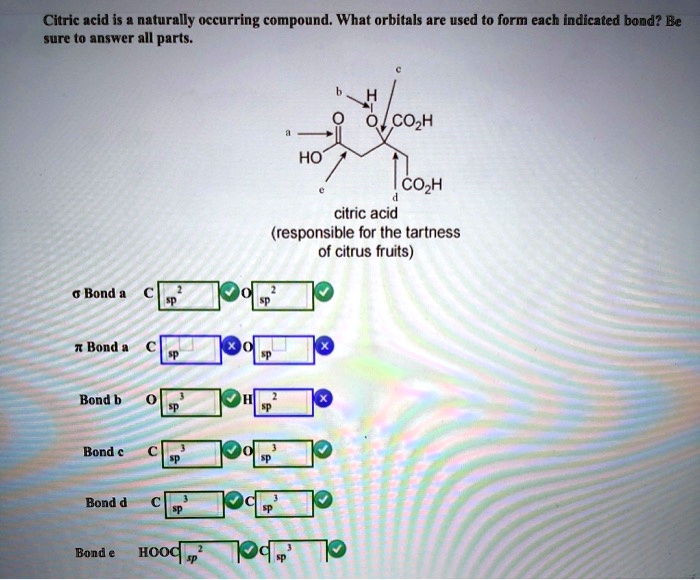
Solved Citric acid is a naturally occurring compound. What
In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two.
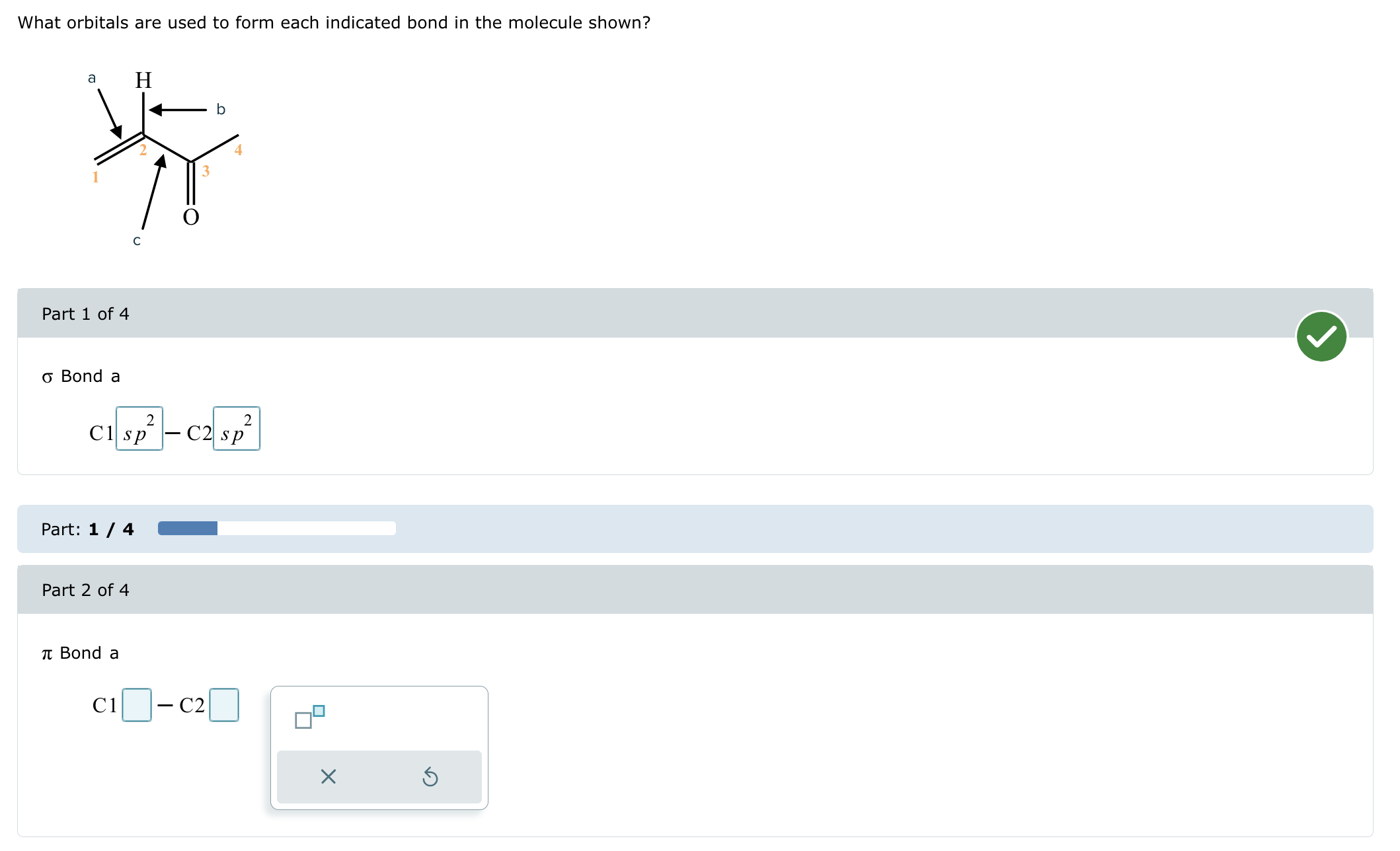
Solved What orbitals are used to form the indicated bond?
In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules.
SOLVED Citric acid is a naturally occurring compound. What orbitals
In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules.
Solved What orbitals are used to form each indicated bond in
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two.
citric acid is naturally occurring compound what orbitals are used to
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two.
Solved What orbitals are used to form each indicated bond in
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two.
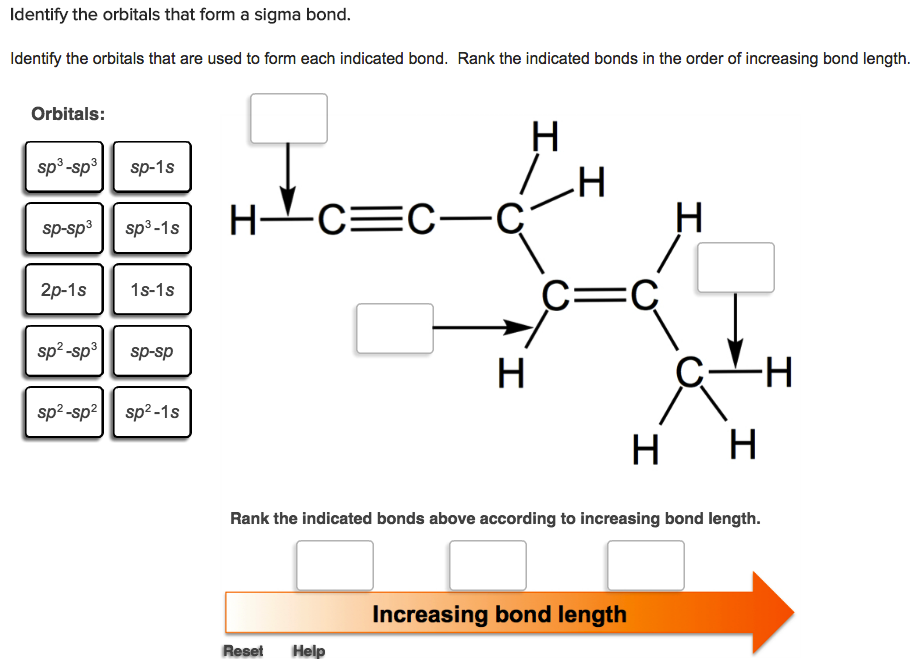
Bond strength is linked to the hybridization of the orbitals used to
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two.
Chemistry Archive June 12, 2016
In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two.
SOLVED Citric acid is naturally occurring compound What orbitals
In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two.
Valence Bond Theory Is Most Often Used To Describe Bonding In Organic Molecules.
In molecular orbital theory, bonds are formed from the overlap of atomic orbitals, and there are two. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two.